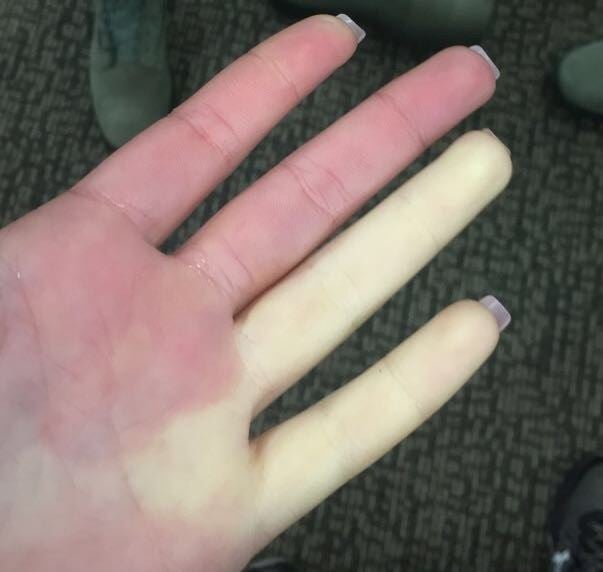
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud’s phenomenon, is a rare medical condition that limits blood supply to fingers, and sometimes to the toes, causing them to temporarily turn white or blue.
Named after physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862, this rare condition can be described as an overreaction to stimuli like cold or stress. In the case of the former, the body tries to conserve heat by slowing down the flow of blood to the farthest points, such as the fingers. To do that, the small arteries that carry blood to those points constrict, thus causing the extremities to temporarily turn white, and then blue, due to the prolonged lack of oxygen in the affected area.