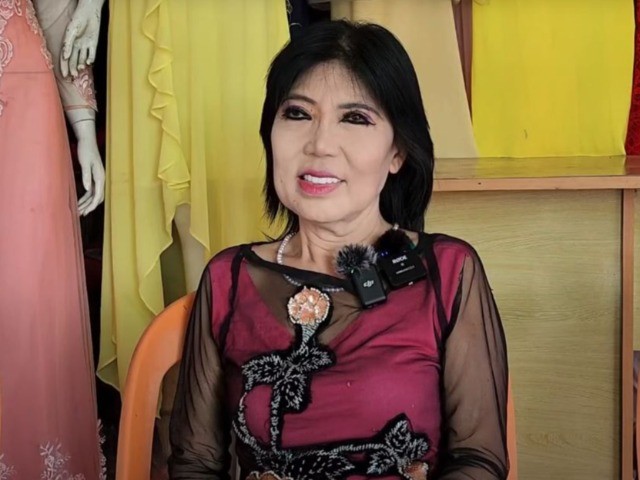
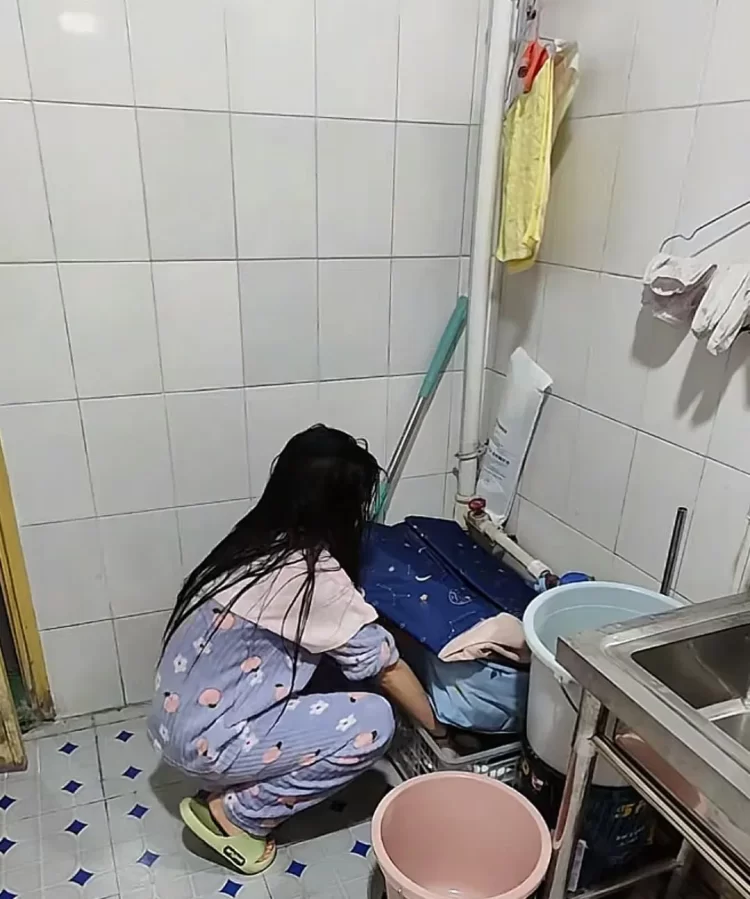
A Vietnamese woman has been dubbed a “sleepless mutant” because of her alleged ability to shun sleep completely. She claims to have remained awake continuously for the last three decades.
49-year-old Nguyen Ngoc My Kim is known as “the seamstress who never sleeps” in her home province of Long An, a nickname she gladly accepts because it apparently suits her. Every time Miss Kim’s reputation attracted the attention of the media, she confirmed that she hadn’t slept in several decades, adding that the complete lack of sleep hadn’t affected her health at all. However, the Vietnamese seamstress has always been quick to point out that she wasn’t born with the ability to function without sleep, she conditioned herself to stay up late ever since she was a little girl. At first, she would lose sleep because she loved reading late into the night, and later, when she started working as a seamstress, she worked late in order to complete her orders. At one point, she didn’t feel the need to sleep at all, so she didn’t.