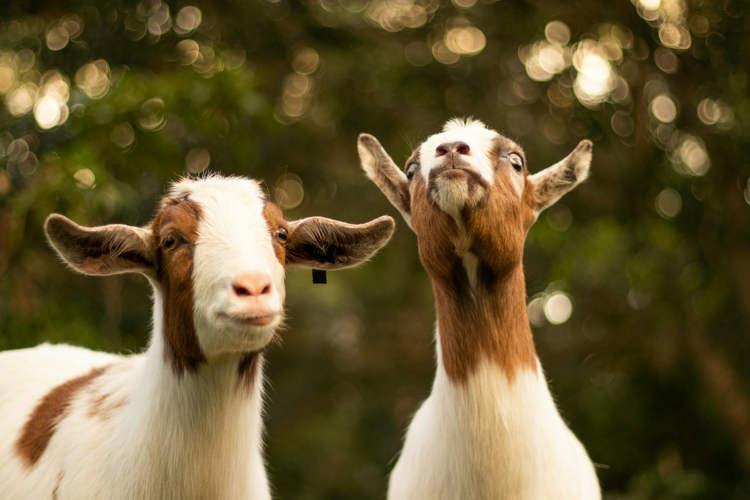
Scientists are trying to understand how a herd of goats not only survived but thrived on an isolated island in northeastern Brazil for over two centuries without any known fresh water source.
It’s not clear how exactly the goats originally wound up on Santa Bárbara, one of the five volcanic islands that make up the Abrolhos archipelago, about 70 kilometers off the coast of Bahia, but scientists believe they were brought and left there by colonizers. Livestock like goats, pigs, and poultry made for a reliable food source, but they were usually left behind when colonization failed. Their presence on Santa Bárbara Island has been documented for more than 250 years, according to historical records, which is remarkable if we take into account that the small island has no known fresh water sources. Despite this “inconvenience,” the goats thrived on the dry, windy island to the point where they had to be relocated in order to protect endemic plants and animals.